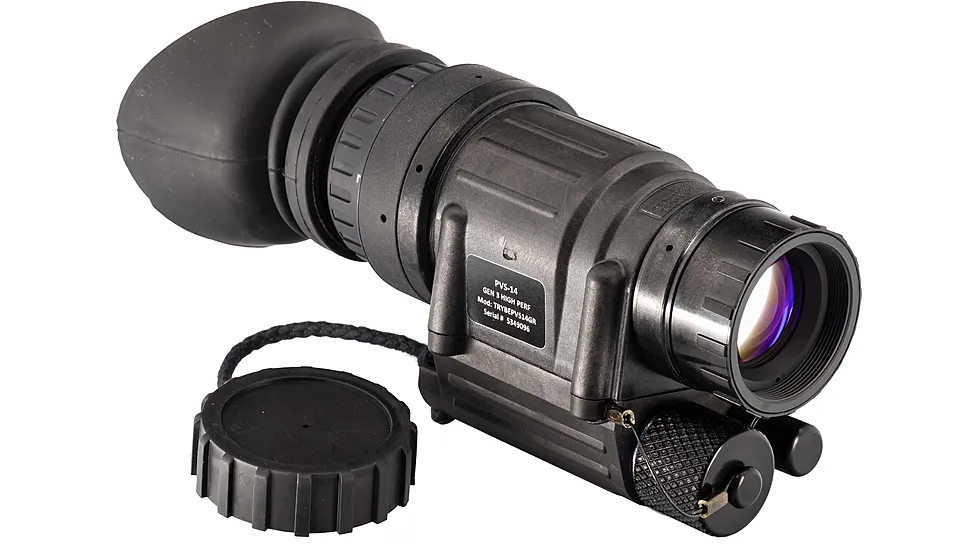
A Night Vision Device (NVD), also known as a Night Observation Device (NOD), is an electronic optic that allows you to see in low or no-light conditions using image intensification technology. Most NVD images are monochrome, but some digital night vision offers full-color images. Night Observation Devices are primarily monoculars or binoculars.
A Night Vision Device (NVD), also known as a Night Observation Device (NOD), is an electronic optic that allows you to see in low or no-light conditions using image intensification technology. Most NVD images are monochrome, but some digital night vision offers full-color images. Night Observation Devices are primarily monoculars or binoculars.![]()
A monocular is an NV product that has one eyepiece and one objective. A night vision monocular has many advantages and is one of the most versatile night vision devices. They are typically considered handheld units; however, many can be head-mounted and weapon-mounted. One of the most significant benefits of a monocular over a binocular or biocular is that you always have one eye that is adjusted to the ambient lighting conditions. This is particularly useful for users who constantly move from dark to lighter conditions where night vision might not be required.
Night vision binoculars are similar to daylight binoculars in that they offer two eyepieces and two front lenses with the addition of an NV intensifier tube. A night vision binocular only uses one intensifier tube system, so it usually doesn't offer better performance or range than a monocular. Still, it will provide more comfortable viewing since you use both eyes and provides a wider field of view. However, an NV binocular will also be heavier and more expensive than an NV monocular.
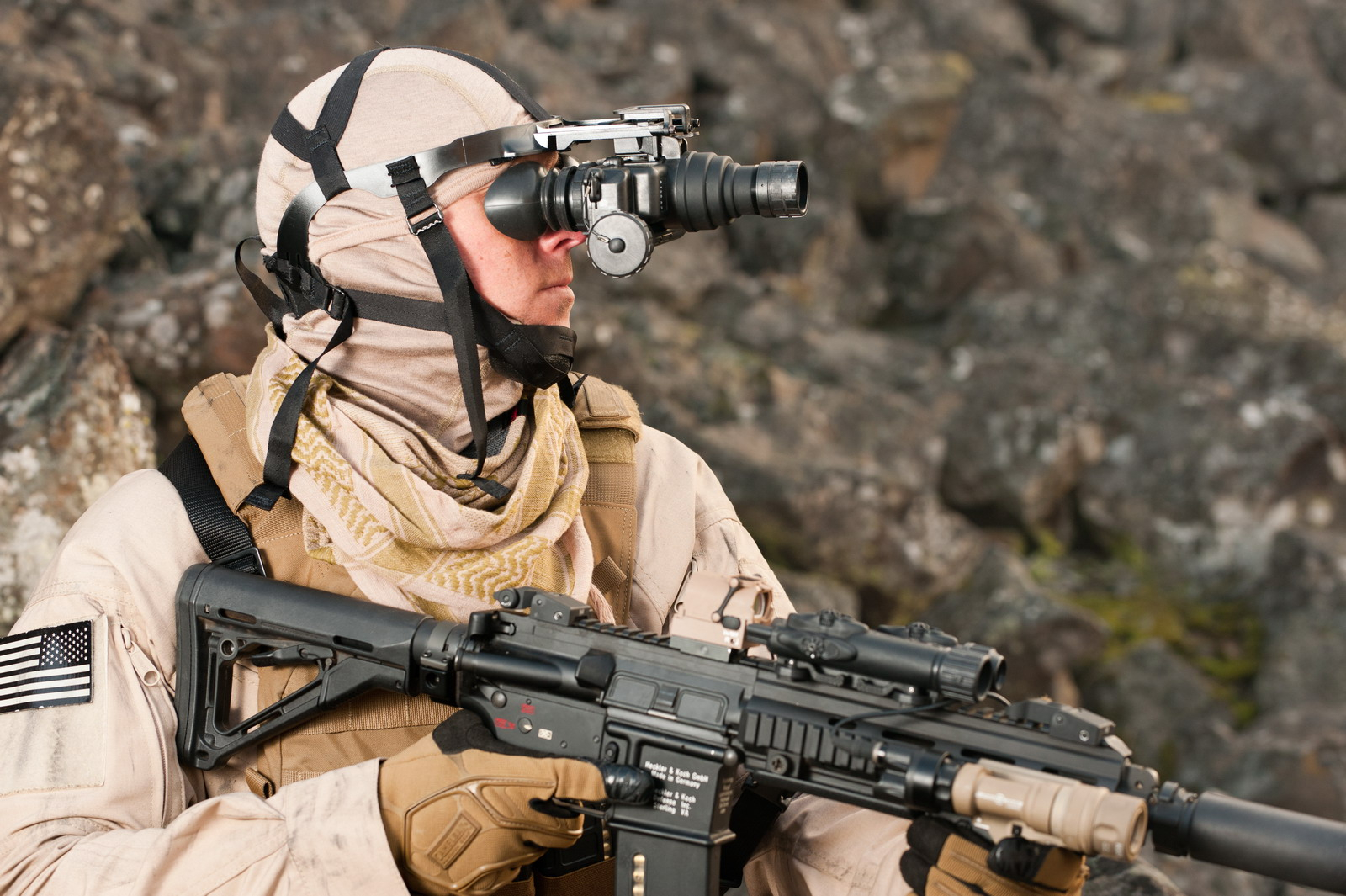 A night vision goggle is any unit that comes with a headset. It comes in three versions:
A night vision goggle is any unit that comes with a headset. It comes in three versions:
Monocular goggles: As the name suggests, this goggle uses a monocular mounted to a headset. This is the lightest and least expensive type of night vision goggle (night vision system). Still, since you are using only one eye and one optical system, it will not be as comfortable to use as a system with two eyepieces, nor will it provide any depth perception.
Bi-ocular goggles: The bi-ocular goggles feature two eyepieces but only one front lens. This improves viewing comfort over a monocular goggle, but because there is only one front lens, there is no improvement in depth perception over a monocular.
Binocular goggles: The binocular goggle uses two eyepieces and two front lenses. This not only provides better viewing comfort than a monocular, but it also provides depth perception since it uses two optical systems. This is an essential feature if you use a goggle while in motion, such as when walking or even driving off-road.
Generating a night vision device product will determine many things, principally performance and price. There are 4 generations of night vision in use as well as digital night vision.
Generation 1 Night Vision
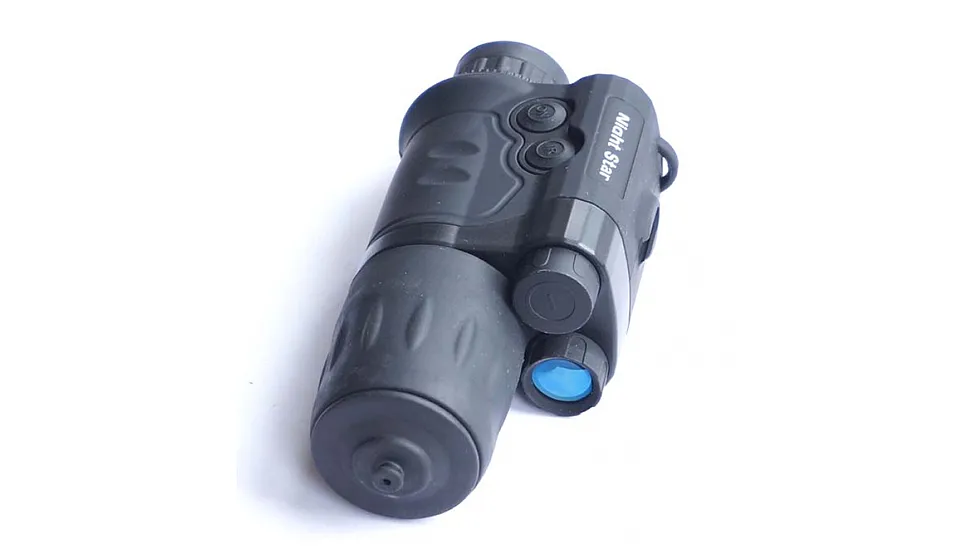 This is the least expensive and oldest technology in night vision. All Generation 1 Night Vision Devices have roughly similar performance. Keep in mind, if a product is listed as "Gen 1+", this indicates a current production tube, not a better tube grade. The only features other than the intensifier tube that affects Gen 1 performance are objective size (significant objectives supply more light), magnification (more is NOT better- this is a low-resolution product), and the IR illuminator (needed by all Gen 1 products under harsh conditions). If you plan to use a night vision device in a marine environment, use a waterproof model.
This is the least expensive and oldest technology in night vision. All Generation 1 Night Vision Devices have roughly similar performance. Keep in mind, if a product is listed as "Gen 1+", this indicates a current production tube, not a better tube grade. The only features other than the intensifier tube that affects Gen 1 performance are objective size (significant objectives supply more light), magnification (more is NOT better- this is a low-resolution product), and the IR illuminator (needed by all Gen 1 products under harsh conditions). If you plan to use a night vision device in a marine environment, use a waterproof model.
Gen 1 units are easily identified. Gen 1 units require a few seconds to power up or down and will always have some pronounced optical distortion, usually fish-eye distortion, at the edge of the field. Gen 1 units can be used to about 75-100 yards to detect man-sized objects under average conditions and perhaps more under ideal conditions, say full moonlight. Detection range is the range in which a target will present a recognizable silhouette. Recognition range is when a target begins to show recognizable detail. For most Gen 1 units, this will typically be 50-75 yards or less for a man-sized object. It is important to understand that smaller targets reduce detection and recognition range.
Generation 2 Night Vision
The biggest gain in performance occurs between Gen 1 and Gen 2. With a Gen 2 tube, you get much less distortion at the edge of the field, a screen with better contrast and resolution, better light amplification (less reliance on an IR for supplemental light), and improved tube life. One significant difference between Gen 1 and Gen 2 is the addition of the Micro Channel Plate. The MCP multiplies the number of electrons flowing from the photocathode by thousands. This feature dramatically increases the resolution and image quality. This all translates into a greater range for both detection and recognition, typically another 50 to 75 yards on both, depending on the grade and type of tube.
Gen 2 also introduces options for grade and type of intensifier tube. To check performance on a 2nd Generation Night Vision Device, you need to check for both resolution (lp or lpm) and type of tube. Special XD Gen 2 tubes, HDT Gen 2 tubes, and SHD3 Gen 2 tubes approach Gen 3 Night Vision Device in performance, but also in price. They truly do bridge the gap between Gen 2 and Gen 3. The most common measure of tube performance that should always be checked on Gen 2 tubes and higher tubes is resolution, stated in line pairs per millimeter (lpm) or sometimes just abbreviated as lp. As the resolution goes up, so does the price.
Generation 3 Night Vision
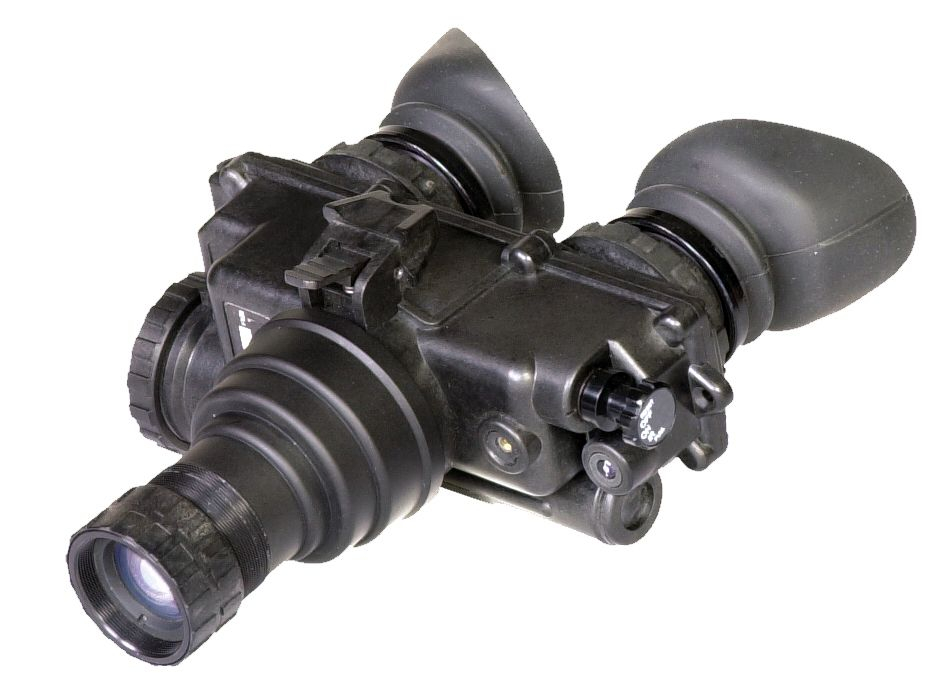 This is the highest generation of night vision technology commonly available and the generation currently employed by most military units and other serious users. Generation 3 Night Vision Units, under ideal conditions, can detect human-sized objects at ranges of 300 yards or more. As with Gen 2 units, there are many grades and options offered. Gen 3 tubes also offer vastly improved tube life and rarely, if ever, need to be replaced. All Gen 3 units are variations on the original AN PVS-14 (monocular) and AN PVS-7 (bi-ocular goggles) used by the military.
This is the highest generation of night vision technology commonly available and the generation currently employed by most military units and other serious users. Generation 3 Night Vision Units, under ideal conditions, can detect human-sized objects at ranges of 300 yards or more. As with Gen 2 units, there are many grades and options offered. Gen 3 tubes also offer vastly improved tube life and rarely, if ever, need to be replaced. All Gen 3 units are variations on the original AN PVS-14 (monocular) and AN PVS-7 (bi-ocular goggles) used by the military.
The most common measure of tube performance that should first be checked on Gen 3 units is resolution, stated in line pairs per millimeter (lpm) or sometimes just abbreviated as lp. Other measures used for grading Gen 3 intensifier tubes include signal-to-noise ratio and screen quality (evenness of brightness and lack of dark spots). However, these specifications are seldom listed or stated by the manufacturer.
A grading system based on letters is sometimes used as follows for Gen 3. Intensifier tubes designated as Mil-Spec must meet minimum military standards for all tube measurements and specifications. Since the origins of NV are military, this is as good as it gets in Night Vision performance. This is also the most expensive and challenging to obtain a grade of NV, especially during wartime. Next are tubes that do not meet mil-spec standards. These are typically referred to as commercial grades. A commercial Grade A tube typically falls short of mil-spec in just one measurement, often with only a minor dark spot on the screen. It may otherwise offer as much resolution as a mil-spec tube. Check the specs. A Grade B commercial tube typically falls short of mil-spec in more than one measurement, though the lower price may make it a good option.
Generation 4 Night Vision
This generation of night vision optics is not commonly seen or produced and was developed as an option for the military, who chose not to adopt it. Generation 4 Night Vision Devices are not as affected by bright light as other generations of NV, but tube life is reduced compared to a Gen 3. Performance is otherwise on par with the best Gen 3 options.
Digital Night Vision
The same technology used in digital cameras, CCD, and CMOS chips to collect light is also used in digital night vision equipment. Like televisions and cell phones, advances are being made rapidly. The first "digital viewers" to appear on the market were on par with a typical Gen 1 unit, but newer versions of digital night vision monoculars and riflescopes are much better.
The advantages of going digital are significant. A digital monocular with Gen 2-like performance will be less than half the price of a standard Gen 2 night vision monocular. Many digital night vision devices can record directly on the device, either to internal memory or on a memory card. This circumvents the need to find an external recording device and compatible adapter, a problem with most conventional NV units. Lastly, digital units are not damaged by exposure to bright light, so that they can be used safely during the day and at night. They are available as monoculars, binoculars, riflescopes, and clip-ons.
Night Vision Magnification
 Night vision technology is about seeing in the dark; it is not about seeing great distances. Simply put, no night vision goggles, night vision binoculars, or night vision rifle scopes, will have the optical resolution of conventional daytime optics. Because of this resolution limit (screen sharpness), magnification in night vision products is limited. As magnification goes up, image quality in night vision goes down. Excess magnification in this technology degrades the image to the point of being useless. The best image quality in conventional night vision technology is usually obtained at 1x (normal vision, no magnification) to about 3x. Field of view, image steadiness, and overall ease of use are also better at these lower magnifications. Digital night vision can offer greater magnification ranges with less decline in image quality.
Night vision technology is about seeing in the dark; it is not about seeing great distances. Simply put, no night vision goggles, night vision binoculars, or night vision rifle scopes, will have the optical resolution of conventional daytime optics. Because of this resolution limit (screen sharpness), magnification in night vision products is limited. As magnification goes up, image quality in night vision goes down. Excess magnification in this technology degrades the image to the point of being useless. The best image quality in conventional night vision technology is usually obtained at 1x (normal vision, no magnification) to about 3x. Field of view, image steadiness, and overall ease of use are also better at these lower magnifications. Digital night vision can offer greater magnification ranges with less decline in image quality.
IR Illumination for Night Vision Googles
An IR illuminator is an excellent addition to any conventional night vision device. It is mandatory when that device is used in total darkness, for instance, in the confines of a darkened building or on an overcast/moonless night. All Generation 1 and digital night vision units will need the assistance of an IR illuminator. These illuminators can be laser or LED-based. IR lasers are also helpful night vision accessories used for signaling/designating targets and aiming weapons.